Category Archives: Java
Request body too large. The max request body size is 30000000 bytes.
环境:Windows, Linux发布.net 6 API 发起接口请求报错:Request body too large. The max request body size is 30000000 bytes. 解决方式,Startup.cs添加如下代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
//接口请求限制 services.Configure<KestrelServerOptions>(options => { options.Limits.MaxRequestBodySize = int.MaxValue; }); |
下面是github的issue,基本上可以解决大部分请求遇到的大小限制问题,可根据自己需要添加相关代码: https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/issues/20369 from:https://blog.csdn.net/The_Moon_/article/details/127996098
View Detailsorg.springframework.web.multipart.MaxUploadSizeExceededException: Maximum up解决方案
application.properties
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=100MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB spring.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold=0 spring.servlet.multipart.location=/usr/local/project/file spring.servlet.multipart.resolve-lazily=false |
application.yml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
spring.servlet: multipart: enabled: true location: /usr/local/project/file max-file-size: 100MB max-request-size: 100MB file-size-threshold: 0 resolve-lazily: false |
from:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44730827/article/details/115719202
View DetailsJava 初始化 List 的几种方法
最常见的初始化 List 方法为:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
List<String> languages = new ArrayList<>(); languages.add("Java"); languages.add("PHP"); languages.add("Python"); System.out.println(languages); |
但是实际上,我们并不会直接使用 new ArrayList 来初始化 List。 你可以使用 Guava 的 newArrayList 来直接初始化。 List<String> languages = Lists.newArrayList(); 上面 2 种方法初始化的 List 是可变的,因此你可以对初始化成功的 List 进行添加和删除。 Arrays 使用这个方法初始化的 List 是不可变的。 考虑使用下面的代码来初始化一个 List。 List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(1,2); Arrays 是 JDK 的一个类,你可以使用这个类来初始化一个 List。 考察下面的代码:
|
1 2 |
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(1,2); list1.add(3); |
将会给你一个:java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 异常。 这是一个运行时错误,不是编译错误。 因此你在编译的时候是不会提示的。 List 使用这个方法初始化的 List 是不可变的。 考虑使用下面的代码来初始化一个 List。 List<Integer> list = List.of(1,2); List 是 JDK 的一个类,你可以使用这个类来初始化一个 List。 考察下面的代码:
|
1 2 |
List<Integer> list1 = List.of(1,2); list1.add(3); |
将会给你一个:java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 异常。 将不可变 List 变成可变 如果 List 是不可变的。 我们可以使用 new ArrayList<> 来包装下就可以了 考察下面的代码:
|
1 2 |
List<Integer>list2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1,2)); list2.add(3); |
如果使用上面的代码的话,你创建的 List 就可以是可变的了,可以对创建的 List 进行修改和删除。 Java 初始化 List 的几种方法 – Java […]
View DetailsSpring Boot多环境文件配置
在实际开发项目中,我们开发环境、测试环境、补丁环境都是有不同的配置的。各个环境可能用不同的数据库,为了便于开发,spring提供了多环境配置文件切换功能。比如:application-dev.yml表示测试环境配置、application-test.yml表示测试环境配置、application-prod.yml表示补丁环境配置、application.yml则是默认环境。如此,我们让那个配置生效,只需要指定对应的配置文件即可。
View DetailsSpring Boot 打包后(jar包) 实现文件上传
文件上传是一个项目最基础的功能,按道理说应该有不会有多困难,但恶心就恶心在 SpringBoot 最方便的优点上!!!
因为 SpringBoot 是内置 Tomcat 的,所以我们并不需要部署到 Tomcat 的服务器,但当打包后(jar包)就出现了问题。
在 IDE 时,因为是正常的文件目录,所以原来的文件上传功能就可以实现,但是打包后,所有的静态文件都变成了 jar 包!!!
这就很头疼,因为当访问 /static 时,实质上访问的是 jar 包文件内容。
Spring Boot整合Ueditor的三种方式
最近前端页面需要使用百度的Ueditor富文本编辑器,本来以为只需要前端适配就可以了,没想到Ueditor需要使用一个服务器统一请求接口,各种百度,历时一天终于弄懂了是怎么一回事,下面是我整了的三种整合的方式,从使用Ueditor的后端代码,到引入Ueditor依赖,到最后完全接管Ueditor后端,都是验证可行的。
View Detailsmaven 构建能够运行的jar文件
用maven来构建过jar文件的朋友可能知道,默认情况下,maven因为不会给我们添加我们项目中需要的依赖,以及不会在MANIFEST.MF文件中添加Main-Class这一条目,造成我们构建完成的jar文件不能通过java -jar命令而直接执行,必须通过java -cp命令,指定类路径来执行.这无疑是非常麻烦的. Google了之后,找到了解决问题的方案.在pom.xml文件中,添加下面的snippet:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
<build> <plugins> <!-- any other plugins --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.5.0</version> <configuration> <descriptorRefs> <descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef> </descriptorRefs> <archive> <manifest> <mainClass>org.longsheng.noobchain.NoobChain</mainClass> </manifest> </archive> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <phase>package</phase> <goals> <goal>single</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> |
把上面的snippet中的mainClass替换成你自己的主类的路径. 然后,就可以通过java -jar命令来执行构建好的jar文件了. 作者:AlstonWilliams 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/868889e32bd6 来源:简书 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
View Detailsmaven引入本地jar不能打入部署包的问题解决
java项目通过maven依赖构建,一般依赖的jar文件都是通过maven配置后从本地仓库查找,如果没有则从中央仓库或私服中远程下载,但有时候引用的jar文件远程仓库中没有,则可以配置本地系统路径来引用,也可以先将本地的jar文件install到本地仓库或上传到远程仓库中。
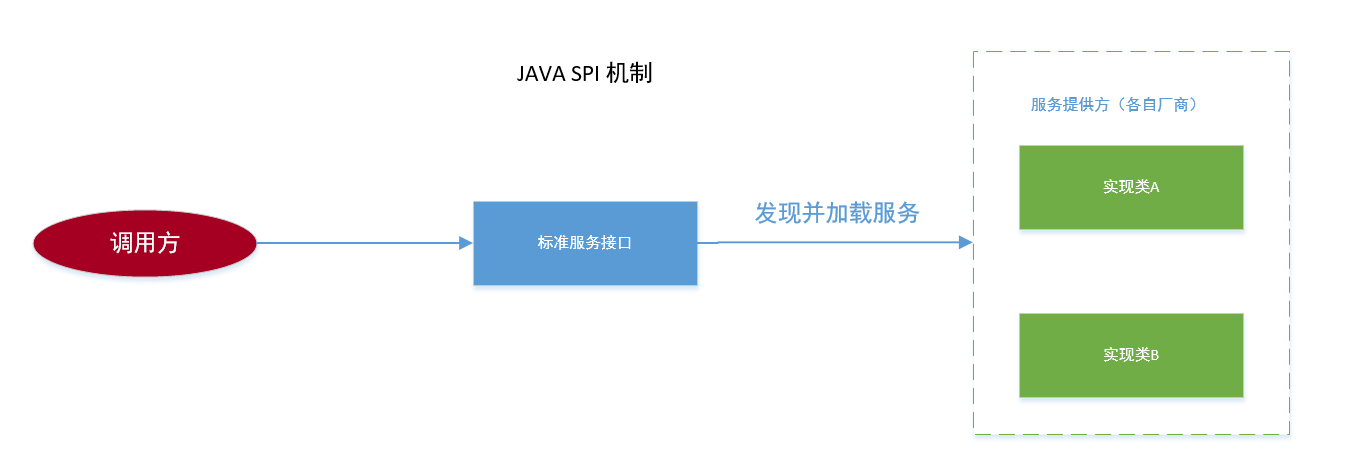
View Details可插拔组件设计机制 —SPI
SPI 的全称是 Service Provider Interface, 即提供服务接口;是一种服务发现机制,SPI 的本质是将接口实现类的全限定名配置在文件中,并由服务加载器读取配置文件,加载实现类。这样可以在运行时,动态为接口替换实现类。正因此特性,我们可以很容易的通过 SPI 机制为我们的程序提供拓展功能。
View Detailsmaven引jar包
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.longsheng</groupId> <artifactId>itemName</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> <scope>system</scope> <systemPath>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/lib/xxxx.jar</systemPath> </dependency> |
View Details