移动端:div在手机页面上随意拖动/拖拽
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 |
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <title>弹窗</title> <meta charset="utf-8"> <script type="text/javascript" src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.11.0.min.js"></script> <style> body{margin:0;padding:0;} .barrage{position:fixed;display:block;top:0;} .barrage_name{width:70px;height:70px;background:-webkit-gradient(linear,0 0,100% 100%,from(#f00), to(#0f0));border-radius:50%;} .barrage_name_hover{width:70px;height:70px;background:-webkit-gradient(linear,0 0,100% 100%,from(#ff0), to(#00f));border-radius:50%;} .col1{color:#fff;display: block;padding: 17px;text-align: center;} </style> </head> <body> <div class="barrage" id="barrage"> <div class="barrage_name" id="barrage_name"> <span class="col1">打开弹幕</span> </div> </div> <div> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> <p>我是来打酱油的</p> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> $(function(){ var cont=$("#barrage"); var contW=$("#barrage").width(); var contH=$("#barrage").height(); var startX,startY,sX,sY,moveX,moveY; var winW=$(window).width(); var winH=$(window).height(); var barrage_name=$("#barrage_name"); var barrage_frame=$("#barrage_frame"); var body=$("body"); cont.on({//绑定事件 touchstart:function(e){ startX = e.originalEvent.targetTouches[0].pageX; //获取点击点的X坐标 startY = e.originalEvent.targetTouches[0].pageY; //获取点击点的Y坐标 //console.log("startX="+startX+"************startY="+startY); sX=$(this).offset().left;//相对于当前窗口X轴的偏移量 sY=$(this).offset().top;//相对于当前窗口Y轴的偏移量 //console.log("sX="+sX+"***************sY="+sY); leftX=startX-sX;//鼠标所能移动的最左端是当前鼠标距div左边距的位置 rightX=winW-contW+leftX;//鼠标所能移动的最右端是当前窗口距离减去鼠标距div最右端位置 topY=startY-sY;//鼠标所能移动最上端是当前鼠标距div上边距的位置 bottomY=winH-contH+topY;//鼠标所能移动最下端是当前窗口距离减去鼠标距div最下端位置 }, touchmove:function(e){ e.preventDefault(); moveX=e.originalEvent.targetTouches[0].pageX;//移动过程中X轴的坐标 moveY=e.originalEvent.targetTouches[0].pageY;//移动过程中Y轴的坐标 //console.log("moveX="+moveX+"************moveY="+moveY); if(moveX<leftX){moveX=leftX;} if(moveX>rightX){moveX=rightX;} if(moveY<topY){moveY=topY;} if(moveY>bottomY){moveY=bottomY;} $(this).css({ "left":moveX+sX-startX, "top":moveY+sY-startY, }) }, }) }) </script> </html> |
为了兼容PC和移动端,想出了以下办法:
拖动时候用到的三个事件: mousedown 、 mousemove 、 mouseup 在移动端都不起任何作用。毕竟移动端是没有鼠标的,查资料后发现,在移动端与之相对应的分别是: touchstart 、 touchmove 、 touchend 事件。还有一点要注意的是在PC端获取当前鼠标的坐标是: event.clientX 和 event.clientY ,在移动端获取坐标位置则是: event.touches[0].clientX 和 event.touches[0].clientY 。下面就来说说怎么实现这个效果吧,先看一下效果:
PC端 :
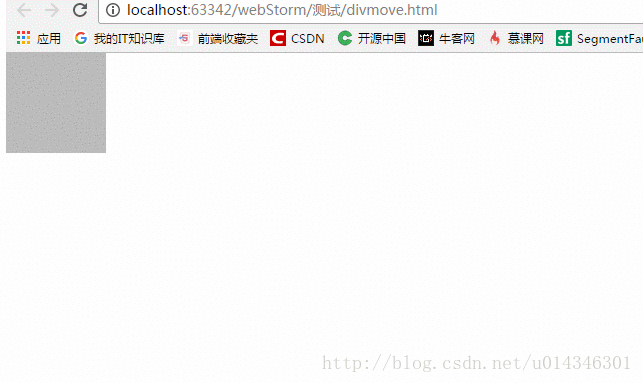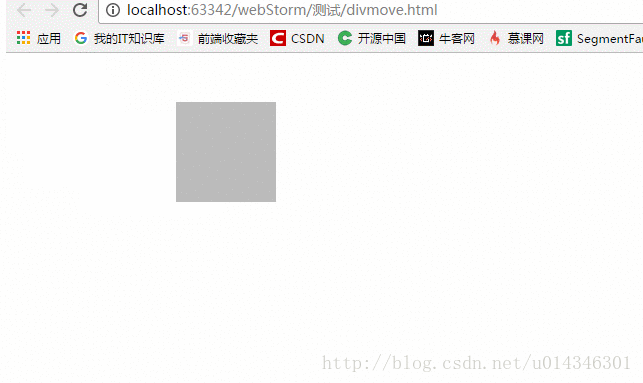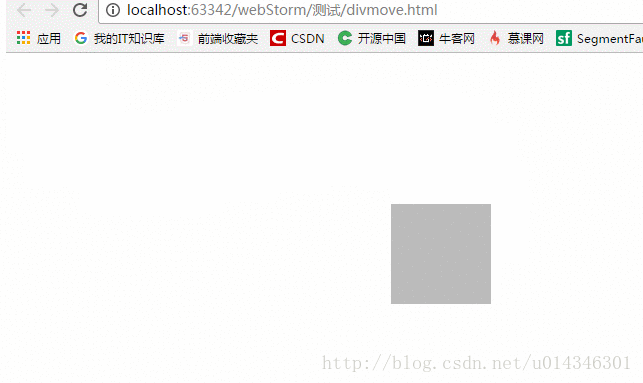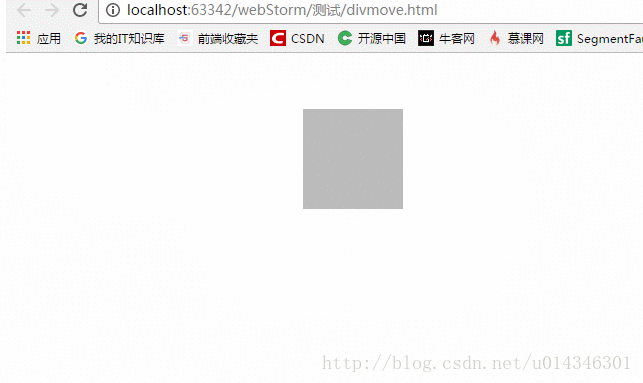
移动端 :

先来分析一个拖动的流程,以PC端为例,首先是鼠标按下( mousedown 事件),然后移动( mousemove 事件),最后释放鼠标( mouseup 事件),首先要设置一个变量记录鼠标是否按下,在鼠标按下的时候,我们做一个标记,然后需要记录一下鼠标当前的坐标,还有这个div当前的偏移量,当鼠标开始移动的时候,记录下鼠标当前的坐标,用鼠标当前的坐标减去鼠标按下时的坐标再加上鼠标按下时div的偏移量就是现在div距离父辈元素的距离,当鼠标释放的时候将标记改为鼠标已经释放。下面来看一下代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
var flag = false; //是否按下鼠标的标记 var cur = { //记录鼠标按下时的坐标 x:0, y:0 } var nx,ny,dx,dy,x,y ; //鼠标按下时的函数 function down(){ flag = true; //确认鼠标按下 cur.x = event.clientX; //记录当前鼠标的x坐标 cur.y = event.clientY; //记录当前鼠标的y坐标 dx = div2.offsetLeft; //记录div当时的左偏移量 dy = div2.offsetTop; //记录div的上偏移量 } //鼠标移动时的函数 function move(){ if(flag){ //如果是鼠标按下则继续执行 nx = event.clientX - cur.x; //记录鼠标在x轴移动的数据 ny = event.clientY - cur.y; //记录鼠标在y轴移动的数据 x = dx+nx; //div在x轴的偏移量加上鼠标在x轴移动的距离 y = dy+ny; //div在y轴的偏移量加上鼠标在y轴移动的距离 div2.style.left = x+"px"; div2.style.top = y +"px"; } } //鼠标释放时候的函数 function end(){ flag = false; //鼠标释放 } |
然后在将事件加入到这个div中即可,下面再来看一个在移动端需要做些什么,首先是事件不同,只需要在添加移动端的 touchatart 、 touchmove 、 touchend 就可以了,还有一个不同的时移动端获取坐标是 event.touches[0].clientX 和 event.touches[0].clientY ,这也很简单,只要加上判断就可以了,如果是PC端就使用event,如果是移动端就使用 event.touches :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
var touch ; if(event.touches){ touch = event.touches[0]; }else { touch = event; } |
还有一点要注意,在移动端拖动div的时候移动端的页面会自动产生滑动效果,所以还需要在 touchmove 的是给页面添加一个阻止默认事件的函数。
下面是整个代码,可以在Chrome下模拟移动端测试,点击这里查看:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>适配移动端的拖动效果</title> <style> #div1{ height: 1000px; } #div2{ position: absolute; top:0; left:0; width: 100px; height: 100px; background: #bbbbbb; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <div id="div2"></div> </div> <script> var flag = false; var cur = { x:0, y:0 } var nx,ny,dx,dy,x,y ; function down(){ flag = true; var touch ; if(event.touches){ touch = event.touches[0]; }else { touch = event; } cur.x = touch.clientX; cur.y = touch.clientY; dx = div2.offsetLeft; dy = div2.offsetTop; } function move(){ if(flag){ var touch ; if(event.touches){ touch = event.touches[0]; }else { touch = event; } nx = touch.clientX - cur.x; ny = touch.clientY - cur.y; x = dx+nx; y = dy+ny; div2.style.left = x+"px"; div2.style.top = y +"px"; //阻止页面的滑动默认事件 document.addEventListener("touchmove",function(){ event.preventDefault(); },false); } } //鼠标释放时候的函数 function end(){ flag = false; } var div2 = document.getElementById("div2"); div2.addEventListener("mousedown",function(){ down(); },false); div2.addEventListener("touchstart",function(){ down(); },false) div2.addEventListener("mousemove",function(){ move(); },false); div2.addEventListener("touchmove",function(){ move(); },false) document.body.addEventListener("mouseup",function(){ end(); },false); div2.addEventListener("touchend",function(){ end(); },false); </script> </body> </html> |
from:https://www.cnblogs.com/joyco773/p/6519668.html