使用nc(netcat)测试udp协议与端口连通性
我们一般想到测试连通性时第一考虑到的就是使用ping命令。
但是我们知道ping命令使用的是icmp协议,属于tcp/ip协议中的一个子协议,所以我们可以用ping命令来测试tcp的连通性还可以测试延迟情况。tcp相关协议了解可以参考:TCP/IP四层模型讲解【笔记整理通俗易懂版】
但是当我们需要测试udp连接的时候ping命令显然没有任何作用。
这时候我们可以用到netcat,这个命令被誉为是网络中的“瑞士军刀”,功能非常强大,测试udp只是其中的一个功能变通。
在安全领域nc常用来端口监听转发,用的比较多的也是windows版的NC,在运维中需要常用到linux上的nc,而一般linux会默认集成这个命令,根据不同系统命令不同,有的为“nc”,有的为“netcat”,大家可以根据实际系统尝试下。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
netcat 命令一览 [v1.10] connect to somewhere: netcat [-options] hostname port[s] [ports] … listen for inbound: netcat -l -p port [-options] [hostname] [port] options: -g gateway source-routing hop point[s], up to 8 -G num source-routing pointer: 4, 8, 12, … -h this cruft -i secs delay interval for lines sent, ports scanned -l listen mode, for inbound connects -n numeric-only IP addresses, no DNS -o file hex dump of traffic -p port local port number -r randomize local and remote ports -s addr local source address -t answer TELNET negotiation -u UDP mode -v verbose [use twice to be more verbose] -w secs timeout for connects and final net reads -z zero-I/O mode [used for scanning] port numbers can be individual or ranges: lo-hi [inclusive] 基本格式:nc [-options] hostname port[s] [ports] … nc -l -p port [options] [hostname] [port] -d 后台模式 -e prog 程序重定向,一旦连接,就执行 [危险!!] -g gateway source-routing hop point[s], up to 8 -G num source-routing pointer: 4, 8, 12, … -h 帮助信息 -i secs 延时的间隔 -l 监听模式,用于入站连接 -L 连接关闭后,仍然继续监听 -n 指定数字的IP地址,不能用hostname -o file 记录16进制的传输 -p port 本地端口号 -r 随机本地及远程端口 -s addr 本地源地址 -t 使用TELNET交互方式 -u UDP模式 -v 详细输出–用两个-v可得到更详细的内容 -w secs timeout的时间 -z 将输入输出关掉–用于扫描时 端口的表示方法可写为M-N的范围格式。 |
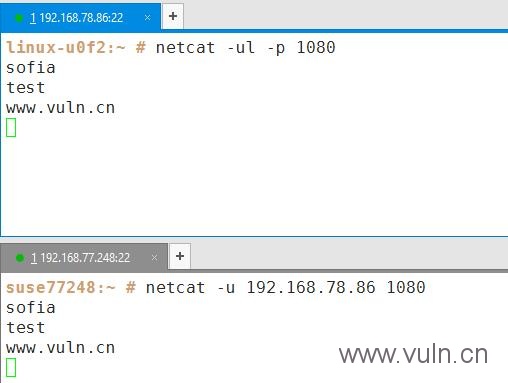
测试udp连接方法
a机器上运行:
nc -ul 1080
或:netcat -ul -p 1080
#使用udp模式监听1080 端口
b机器上运行:
nc -u x.x.x.x 1080
或:netcat -u x.x.x.x 1080
#使用udp模式向该ip的1080端口发送信息。
效果如图,在任意一边输入内容,另一边则会收到相应内容,以此就可以测试该端口的udp连接是否通常。
from:http://www.vuln.cn/2922